
Let Customers Pull
Kanban System
What is it?
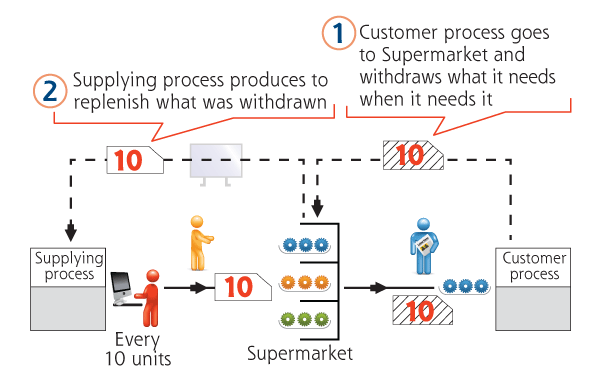
A method of using visual signals (kanban) for triggering or controlling the flow of materials between processes internally or with outside suppliers.
Typical Kanban card
Why use it?
- Prevents overproduction as demand varies
- Provides specific production instructions of timing and quantity
- Serves as a quick visual control tool for production (Are you ahead or behind schedule?)
- Establishes a tool for continuous improvement (reduction of the number of kanban)
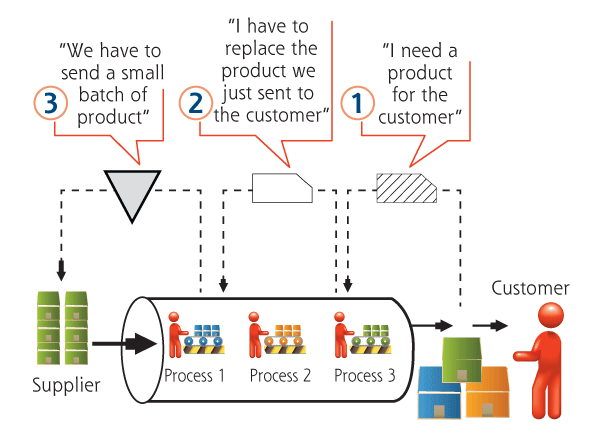
The Kanban “Talk”
The Six Kanban Rules
Follow these six kanban rules:
- Downstream processes always come to withdraw
- Produce only the quantity withdrawn
- Don’t send defects to the next process
- Kanban should be attached to the actual parts containers
- For kanban to work, production must be leveled
- The best kanban is not needing a kanban
How do I do it?
- Validate three conditions:
- Flow cannot be achieved between the two processes at this time. Remember rule number 6.
- Equipment, process and people are reliable most of the time, at least 80% of the time.
- Production has been leveled to avoid overcapacity and out of stock items
- Calculate the number of kanban cards (N):
N = [(Average Demand x Lead Time) + Buffer Stock + Safety Stock] / Container Size
Buffer = Inventory due to sudden fluctuations in customer orders
Safety Stock = Inventory due to reliability issues in the process
- Define the kanban cards and process for production and withdrawal. Train all participants by simulating the actual process
- Implement and follow until kanban system is stable

Kanban systems are used only after a line has been stabled and balanced.
Next:
7. Pursue Perfection